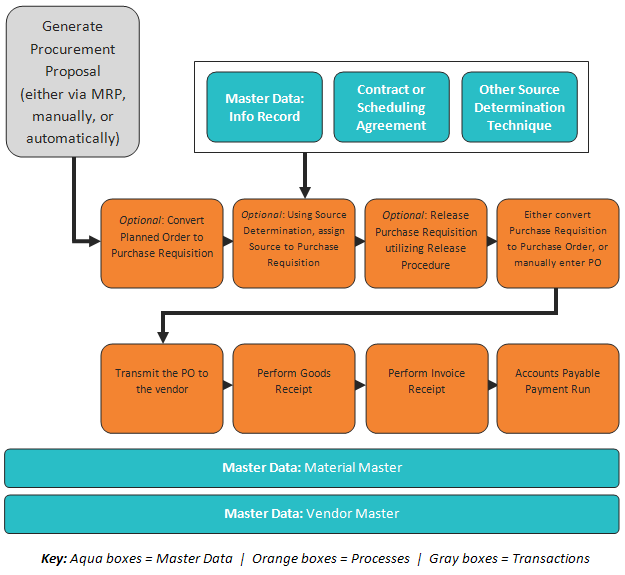
Sap Mm Configuration Manual Pdf
SAP MM i About the Tutorial SAP is an enterprise resource planning software that was basically designed to manage resources, information and activities that are. Introduction to Variant Configuration in R3 Contents. The following topics are covered by this presentation Overview Prerequisite Configuration Profile. WorkOrderChartFlowofEvents-768x974.png' alt='Sap Mm Configuration Manual Pdf' title='Sap Mm Configuration Manual Pdf' />
 The SAP Community is the quickest way for users to solve problems, learn more about SAP solutions, and invent new ways to get things done. Note Your browser does not support JavaScript or it is turned off. Press the button to proceed. View and Download Ricoh SP C400DN user manual online. SP C400DN Copier pdf manual download. Understanding SAP Extended Warehouse Management. SAP Extended Warehouse Management EWM is designed to aid companies in organizing, managing, and improving the efficiency of warehousing environments. In this SAP Press book chapter excerpt, learn the history of the SAP EWM application and discover how this software has evolved to meet the demands of SAP customers. Introduction to SAP Extended Warehouse Management. This text provides you with the information you need to understand the SAP EWM solution, including the functions that it supports, how to set up those functions, and how to get started with a project that will utilize those functions to support your warehouse operations. In this chapter, we will start by providing some background and history on SAPs warehousing applications, tell you how SAP EWM evolved, inform you about the variations of the EWM brand, and tell you who this text is for and how to use it. We hope that the text serves to inform and educate you and help you make the right decisions regarding your EWM implementation. Background and History. In the past few decades, warehouses have evolved from simple receiving, storage, and shipping facilities to full scale, high volume, flow through distribution operations. Global competition has driven businesses to hold less inventory and to get their products to market both faster and with more precise timing than in the past. Competition has also driven both local and global corporations to become leaner and more efficient and to react faster to both changes in the marketplace and in the internal business environment. Constantly shifting business priorities, increasing seasonality of products, faster business cycles, and more frequent mergers and acquisitions are just some of the market conditions that lead to intense pressure on warehouses to increase efficiency while still providing flexibility to the business to allow it to react to changing demands. At the same time, disproportionate increases in costs of labor, raw materials, and real estate threaten to drive warehousing costs higher, impeding companies ability to make a profit. For some companies, this pressure to perform effective logistics operations is too great or comes at too great a cost, and they are increasingly turning to outsourced solutions, such as third party logistics providers, to cost effectively handle the volumes of products and ever changing business requirements. However, this just shifts the burden to a whole new group of people, upon whom the pressures are even more intensified by the need to not only maintain flexibility for a single organization, but to maintain flexibility across multiple organizations. To top it off, those organizations often have very different products, processes, business requirements, and management styles. This increase in pressure on warehouses to do more with less has led to a corresponding increase in the complexity of business processes. In turn, this increasing complexity of business processes then requires both an increase in talent of warehouse managers and an increase in capabilities of the systems that help those managers run their businesses. The evolution of the warehouse management system WMS software industry has run parallel to the changes in the warehousing and distribution marketplace, with ever increasing business process capabilities supported by more and more capable WMSs delivered by companies who specialize in standardized software. Shariah Program Login. However, there are still companies who prefer to run their own bespoke systems filled with functionality specific to their own businesses and supported by armies of programmers. But more and more, those companies are realizing the benefits in the total cost of ownership TCO of using standard software solutions that also meet their business needs. And those companies are turning to software vendors like SAP for their software solutions. Since 1. 97. 2, SAP has specialized in providing standard software solutions for common business processes. Since the first release of R1 a year after the companys founding, SAP has constantly evolved their products to expand into new markets or to match the changing business needs of their customer base. Through the R2 days in the late 1. SAP delivered software to not only meet the needs of back office functions like finance and purchasing, but began to move more and more to the front lines of managing the product manufacturing, sales, and distribution. In the early 1. 99. Bow Master Game For Pc here. SAP delivered its flagship client server product, SAP R3, and it has continued to enhance that application throughout its lifecycle. The SAP R3 product evolved in the early 2. SAP ERP. In the meantime, starting in the late 1. SAP began to deliver, in addition to its core ERP functions, specialized functions for Customer Relationship Management CRM, Supply Chain Management SCM, and Business Warehousing BW. The collective release of these products was dubbed the New Dimension products, representing a new dimension in enterprise software. In the 2. 00. 0s, SAP continued to refine and expand those products, delivering release after release of new and revised functionality. As part of this wave of new and expanded functionality, SAP delivered the first release of SAP EWM in 2. At the time, EWM was part of the SAP SCM solution and could not be delivered separately. Since then, SAP has delivered the capability to deploy EWM as an addon to SAP ERP, allowing EWM to break free from its SCM roots and enjoy its own product naming and branding SAP EWM. In this text, we will discuss SAP EWM, including its history, configuration, implementation, utilization for solving common business problems, and extension to solve implementations specific business problem. We will discuss the functionality of the latest release, SAP EWM 7. Unless otherwise specified, all screenshots and product descriptions are specific to the SAP EWM 7. The Evolution of SAP WMSEven as early as release R2, SAP contained functionality for locating products in the warehouse. At the time, it was a basic locator system, but it provided the baseline for SAPs foray into the warehouse management WM world. In 1. 99. 3, SAP released R3 Release 2. Back then, SAP WM only covered the basics of a warehousing application, namely to track product in multiple bins in the warehouse and assign pallet identification labels, or pallet IDs, to the product in the bin. In SAP parlance, these pallet IDs were known as storage units. Since its initial releases, SAP has extended its WM application with additional functionality including integration to SAP R3 Production Planning, Quality Management, and Logistics Information Systems in SAP R3 Release 3. SAP R3 Human Resources HR in SAP R3 Release 4. Departure Board Software'>Departure Board Software. WM and radio frequency support in SAP R3 Release 4. HU management an Inventory Managementlevel method for tracking pallet IDs across plants, storage locations, and warehouses and packing station capabilities in SAP R3 Release 4. SAP R3 Enterprise 4. Extension Set 1. 1support for yard management, cross docking, and value added services VAS in SAP R3 Enterprise 4. Extension Set 2. 0In parallel, businesses around the world started to use the SAP WM system to manage more and more complex warehouses and distribution centers. As the product grew, the customer base grew with it, and today, SAP WM is deployed by more than 5,0. SAP customers worldwide. In 2. 00. 5, SAP released version 5.
The SAP Community is the quickest way for users to solve problems, learn more about SAP solutions, and invent new ways to get things done. Note Your browser does not support JavaScript or it is turned off. Press the button to proceed. View and Download Ricoh SP C400DN user manual online. SP C400DN Copier pdf manual download. Understanding SAP Extended Warehouse Management. SAP Extended Warehouse Management EWM is designed to aid companies in organizing, managing, and improving the efficiency of warehousing environments. In this SAP Press book chapter excerpt, learn the history of the SAP EWM application and discover how this software has evolved to meet the demands of SAP customers. Introduction to SAP Extended Warehouse Management. This text provides you with the information you need to understand the SAP EWM solution, including the functions that it supports, how to set up those functions, and how to get started with a project that will utilize those functions to support your warehouse operations. In this chapter, we will start by providing some background and history on SAPs warehousing applications, tell you how SAP EWM evolved, inform you about the variations of the EWM brand, and tell you who this text is for and how to use it. We hope that the text serves to inform and educate you and help you make the right decisions regarding your EWM implementation. Background and History. In the past few decades, warehouses have evolved from simple receiving, storage, and shipping facilities to full scale, high volume, flow through distribution operations. Global competition has driven businesses to hold less inventory and to get their products to market both faster and with more precise timing than in the past. Competition has also driven both local and global corporations to become leaner and more efficient and to react faster to both changes in the marketplace and in the internal business environment. Constantly shifting business priorities, increasing seasonality of products, faster business cycles, and more frequent mergers and acquisitions are just some of the market conditions that lead to intense pressure on warehouses to increase efficiency while still providing flexibility to the business to allow it to react to changing demands. At the same time, disproportionate increases in costs of labor, raw materials, and real estate threaten to drive warehousing costs higher, impeding companies ability to make a profit. For some companies, this pressure to perform effective logistics operations is too great or comes at too great a cost, and they are increasingly turning to outsourced solutions, such as third party logistics providers, to cost effectively handle the volumes of products and ever changing business requirements. However, this just shifts the burden to a whole new group of people, upon whom the pressures are even more intensified by the need to not only maintain flexibility for a single organization, but to maintain flexibility across multiple organizations. To top it off, those organizations often have very different products, processes, business requirements, and management styles. This increase in pressure on warehouses to do more with less has led to a corresponding increase in the complexity of business processes. In turn, this increasing complexity of business processes then requires both an increase in talent of warehouse managers and an increase in capabilities of the systems that help those managers run their businesses. The evolution of the warehouse management system WMS software industry has run parallel to the changes in the warehousing and distribution marketplace, with ever increasing business process capabilities supported by more and more capable WMSs delivered by companies who specialize in standardized software. Shariah Program Login. However, there are still companies who prefer to run their own bespoke systems filled with functionality specific to their own businesses and supported by armies of programmers. But more and more, those companies are realizing the benefits in the total cost of ownership TCO of using standard software solutions that also meet their business needs. And those companies are turning to software vendors like SAP for their software solutions. Since 1. 97. 2, SAP has specialized in providing standard software solutions for common business processes. Since the first release of R1 a year after the companys founding, SAP has constantly evolved their products to expand into new markets or to match the changing business needs of their customer base. Through the R2 days in the late 1. SAP delivered software to not only meet the needs of back office functions like finance and purchasing, but began to move more and more to the front lines of managing the product manufacturing, sales, and distribution. In the early 1. 99. Bow Master Game For Pc here. SAP delivered its flagship client server product, SAP R3, and it has continued to enhance that application throughout its lifecycle. The SAP R3 product evolved in the early 2. SAP ERP. In the meantime, starting in the late 1. SAP began to deliver, in addition to its core ERP functions, specialized functions for Customer Relationship Management CRM, Supply Chain Management SCM, and Business Warehousing BW. The collective release of these products was dubbed the New Dimension products, representing a new dimension in enterprise software. In the 2. 00. 0s, SAP continued to refine and expand those products, delivering release after release of new and revised functionality. As part of this wave of new and expanded functionality, SAP delivered the first release of SAP EWM in 2. At the time, EWM was part of the SAP SCM solution and could not be delivered separately. Since then, SAP has delivered the capability to deploy EWM as an addon to SAP ERP, allowing EWM to break free from its SCM roots and enjoy its own product naming and branding SAP EWM. In this text, we will discuss SAP EWM, including its history, configuration, implementation, utilization for solving common business problems, and extension to solve implementations specific business problem. We will discuss the functionality of the latest release, SAP EWM 7. Unless otherwise specified, all screenshots and product descriptions are specific to the SAP EWM 7. The Evolution of SAP WMSEven as early as release R2, SAP contained functionality for locating products in the warehouse. At the time, it was a basic locator system, but it provided the baseline for SAPs foray into the warehouse management WM world. In 1. 99. 3, SAP released R3 Release 2. Back then, SAP WM only covered the basics of a warehousing application, namely to track product in multiple bins in the warehouse and assign pallet identification labels, or pallet IDs, to the product in the bin. In SAP parlance, these pallet IDs were known as storage units. Since its initial releases, SAP has extended its WM application with additional functionality including integration to SAP R3 Production Planning, Quality Management, and Logistics Information Systems in SAP R3 Release 3. SAP R3 Human Resources HR in SAP R3 Release 4. Departure Board Software'>Departure Board Software. WM and radio frequency support in SAP R3 Release 4. HU management an Inventory Managementlevel method for tracking pallet IDs across plants, storage locations, and warehouses and packing station capabilities in SAP R3 Release 4. SAP R3 Enterprise 4. Extension Set 1. 1support for yard management, cross docking, and value added services VAS in SAP R3 Enterprise 4. Extension Set 2. 0In parallel, businesses around the world started to use the SAP WM system to manage more and more complex warehouses and distribution centers. As the product grew, the customer base grew with it, and today, SAP WM is deployed by more than 5,0. SAP customers worldwide. In 2. 00. 5, SAP released version 5.
